Conversational AI on YouTube
NotebookLM Summary
../assets/audio/notebooklm_dig_deeper.wav
Overview
This blog post explores the creation of a prototype browser plugin that analyzes the YouTube Shorts you watch. The goal is to encourage users to actively search and “dig deeper” into topics, rather than passively consuming content from the platform’s recommendation system. The plugin achieves this by generating transcripts of videos, feeding them to a language model, and providing a chat interface for interaction.
The plugin has three main components:
- Transcripts: Extracting audio from YouTube videos and converting it into text.
- GPT API Integration: Using OpenAI’s GPT to generate curiosity-provoking suggestions based on the video content.
- Chat Interface: A simple browser-based chatbox for user interaction.
Transcripts
The first step is to extract audio from YouTube videos and convert it into text using OpenAI’s Whisper model. Below is the code for downloading audio, converting it to a suitable format, and generating transcripts.
Downloading Audio
const fs = require('fs');
const ytdl = require('@distube/ytdl-core');
The ytdl-core library is used to download audio from YouTube. The downloadAudioOnly function filters the video to download only the audio stream and saves it to a specified path.
function downloadAudioOnly(url, audio_path, callback) {
const stream = ytdl(url,
{
filter: 'audioonly',
requestOptions: {
headers: {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36'
}
}
}
);
stream.pipe(fs.createWriteStream(audio_path))
.on('finish', () => {
callback(null, 'Download and save completed');
})
.on('error', (err) => {
callback('Error writing to file: ' + err.message);
});
stream.on('error', (err) => {
callback('Error downloading audio: ' + err.message);
});
}
This function ensures that only the audio is downloaded, which reduces the file size and processing time.
Converting Audio to WAV Format
Once the audio is downloaded, it needs to be converted to a WAV format compatible with the Whisper model. This is done using the ffmpeg-static library.
function convertMP3ToWAV(audio_path_mp3, audio_path_wav){
const ffmpeg = require('ffmpeg-static');
const spawn = require('child_process').spawn;
const ffmpegProcess = spawn(ffmpeg, ['-i', audio_path_mp3, '-ar', '16000', audio_path_wav]);
ffmpegProcess.on('exit', () => {
console.debug('Audio converted successfully!');
});
ffmpegProcess.on('error', (err) => {
console.error('Error converting audio:', err);
});
}
This function uses ffmpeg to convert the MP3 file to a WAV file with a sample rate of 16,000 Hz, which is required for Whisper.
Generating Transcripts
The ytTranscript function orchestrates the process of downloading audio, converting it to WAV, and generating a transcript using Whisper.
async function ytTranscript(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
video_id = get_video_id(url);
audio_path_mp3 = path.join(process.cwd(), 'output/', video_id + '.mp3');
audio_path_wav = path.join(process.cwd(), 'output/', video_id + '.wav');
downloadAudioOnly(url, audio_path_mp3, (error, message) => {
if (error) {
console.error('Error downloading or saving the video:', error);
reject(error);
} else {
console.debug(message);
convertMP3ToWAV(audio_path_mp3, audio_path_wav);
const whisper = require('whisper-node');
(async () => {
try {
const transcript = await whisper.whisper(audio_path_wav, {modelName: "base.en", word_timestamps: false});
const speechText = transcript.map(item => item.speech).join(' ');
const cleanedSpeechText = speechText.replace(/ ([',.!?])/g, '$1');
console.debug(cleanedSpeechText);
resolve(cleanedSpeechText);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error:', error);
reject(error);
}
})();
}
});
});
}
This function:
- Downloads the audio from the YouTube video.
- Converts the audio to WAV format.
- Uses Whisper to generate a transcript of the audio.
GPT API Integration
The next step is to integrate OpenAI’s GPT API to generate curiosity-provoking suggestions based on the video transcript. The following code sets up an Express server to handle requests.
const express = require('express');
const OpenAI = require('openai');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
app.use(express.json({ limit: '10mb' }));
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: <OPENAI_KEY>,
});
app.post('/oracle', async (req, res) => {
const { query, page } = req.body;
try {
const completion = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: 'gpt-4o',
messages: [
{ role: 'system', content: 'You are a fact-finding curiosity machine...' },
{ role: 'user', content: `Context: ${context}, Question: ${query}` },
],
});
const response = completion.choices[0].message.content;
res.json({ response });
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error querying OpenAI:', error);
res.status(500).json({ error: 'Failed to get a response from OpenAI' });
}
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Oracle server listening at http://localhost:${port}`);
});
This server:
- Accepts a query and video URL from the client.
- Retrieves the transcript for the video.
- Sends the transcript and query to GPT to generate a response.
- Returns the response to the client.
Chat Interface
Finally, a simple chat interface is implemented in the browser to allow users to interact with the plugin.
document.getElementById("send").addEventListener("click", () => {
const query = document.getElementById("input").value;
chrome.tabs.query({ active: true, currentWindow: true }, (tabs) => {
chrome.tabs.query(
{ url: ["*://*.youtube.com/*"] },
async (youtubeTabs) => {
if (youtubeTabs.length == 0) {
console.log("No YouTube tab found");
} else {
const currentTab = youtubeTabs[0];
fetch("http://localhost:3000/oracle", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({ query, page: currentTab.url }),
})
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => {
const response = data.response;
const chatDiv = document.getElementById("chat");
chatDiv.innerHTML += `<p><strong>You:</strong> ${query}</p>`;
chatDiv.innerHTML += `<p><strong>Oracle:</strong> ${response}</p>`;
document.getElementById("input").value = "";
chatDiv.scrollTop = chatDiv.scrollHeight;
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error("Error:", error);
});
}
}
);
});
});
This script:
- Captures user input from a chatbox.
- Sends the query and current YouTube video URL to the server.
- Displays the response from GPT in the chatbox.
Conclusion
While the prototype demonstrates how AI can be used to encourage curiosity and deeper exploration of topics, there are so many limitations:
- The chatbox isn’t persistent
- It requires prompting
- It doesn’t interrupt the user with suggestions
- It relies on ytdl, which can be rate limited
- It requires running OpenAI’s whisper model locally
- It requires an unreasonable degree of permission and access to user data in the browser
- There is a fair amount of latency when waiting for responses
Despite all that, it’s pretty neat that you can run Whisper locally on a CPU and have it chat to you about what you watch. It looks like this:
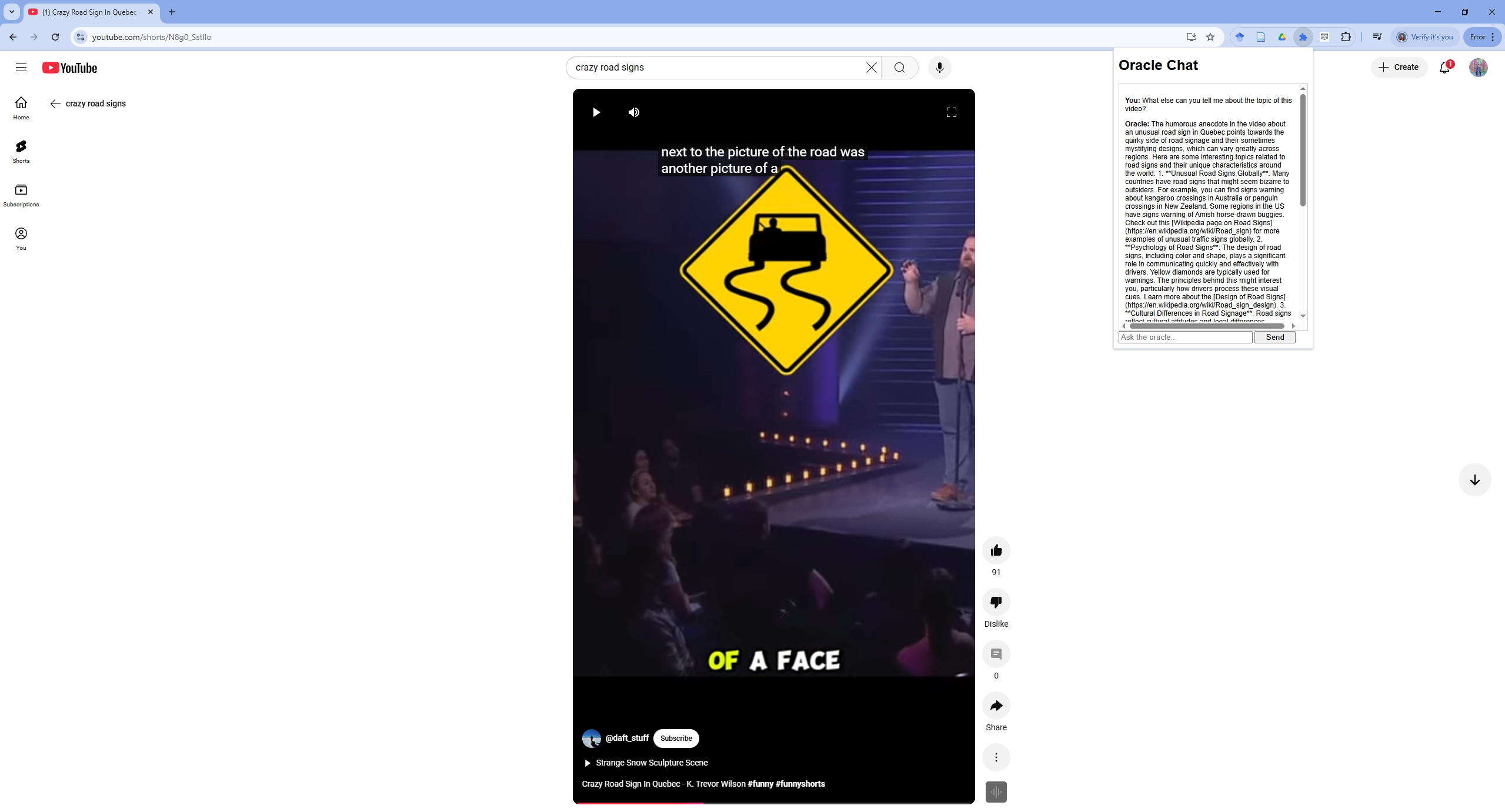
For the full code, checkout this Github repository.